A. Sakurako’s Exam
题目
Today, Sakurako has a math exam. The teacher gave the array, consisting of $a$ ones and $b$ twos.
In an array, Sakurako must place either a ‘+’ or a ‘-‘ in front of each element so that the sum of all elements in the array equals $0$.
Sakurako is not sure if it is possible to solve this problem, so determine whether there is a way to assign signs such that the sum of all elements in the array equals $0$.
实现
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e5+10;
const int mod=1e9+7;
void solve()
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
int now=a+b*2;
while(b>0 and now>=4)
{
b--;
now-=4;
}
while(a>0 and now>=2)
{
a--;
now-=2;
}
if(now==0) cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}
B. Square or Not
题目
A beautiful binary matrix is a matrix that has ones on its edges and zeros inside.

Today, Sakurako was playing with a beautiful binary matrix of size $r \times c$ and created a binary string $s$ by writing down all the rows of the matrix, starting from the first and ending with the $r$-th. More formally, the element from the matrix in the $i$-th row and $j$-th column corresponds to the $((i-1)*c+j)$-th element of the string.
You need to check whether the beautiful matrix from which the string $s$ was obtained could be squared. In other words, you need to check whether the string $s$ could have been build from a square beautiful binary matrix (i.e., one where $r=c$).
实现
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e5+10;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
string s;
cin>>s;
if(sqrt(n)*sqrt(n)!=n)
{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return;
}
s=' '+s;
if(n==4||s==" 1111")
{
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
return;
}
int num=sqrt(n);
for(int i=num+1;i<=n-num;i++)
{
if((i%num==1||i%num==0)&&s[i]=='0')
{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return;
}
if((i%num)!=1&&((i%num)!=0))
{
if(s[i]=='1')
{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return;
}
}
}
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}
C. Longest Good Array
题目
Today, Sakurako was studying arrays. An array $a$ of length $n$ is considered good if and only if:
- the array $a$ is increasing, meaning $a_{i - 1} < a_i$ for all $2 \le i \le n$;
- the differences between adjacent elements are increasing, meaning $a_i - a_{i-1} < a_{i+1} - a_i$ for all $2 \le i < n$.
Sakurako has come up with boundaries $l$ and $r$ and wants to construct a good array of maximum length, where $l \le a_i \le r$ for all $a_i$.
Help Sakurako find the maximum length of a good array for the given $l$ and $r$.
实现
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e3;
const int M=2e5+10;
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
int num=0;
for(;num*(num+1)/2<=r-l;num++)
{
;
}
if(num*(num+1)/2>r-l) num--;
cout<<num+1<<endl;
}
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}
D. Sakurako’s Hobby
题目
For a certain permutation $p$$^{\text{∗}}$ Sakurako calls an integer $j$ reachable from an integer $i$ if it is possible to make $i$ equal to $j$ by assigning $i=p_i$ a certain number of times.
If $p=[3,5,6,1,2,4]$, then, for example, $4$ is reachable from $1$, because: $i=1$ $\rightarrow$ $i=p_1=3$ $\rightarrow$ $i=p_3=6$ $\rightarrow$ $i=p_6=4$. Now $i=4$, so $4$ is reachable from $1$.
Each number in the permutation is colored either black or white.
Sakurako defines the function $F(i)$ as the number of black integers that are reachable from $i$.
Sakurako is interested in $F(i)$ for each $1\le i\le n$, but calculating all values becomes very difficult, so she asks you, as her good friend, to compute this.
$^{\text{∗}}$A permutation of length $n$ is an array consisting of $n$ distinct integers from $1$ to $n$ in arbitrary order. For example, $[2,3,1,5,4]$ is a permutation, but $[1,2,2]$ is not a permutation (the number $2$ appears twice in the array), and $[1,3,4]$ is also not a permutation ($n=3$, but the array contains $4$).
实现
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e5+10;
//const int M=2e5+10;
int dp[N];
int a[N],b[N];
int p[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=p[x]) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
p[i]=i;
}
string s;
cin>>s;
s=' '+s;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
p[find(a[i])]=find(i);
}
map<int,int>mp;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(s[i]=='0') mp[find(i)]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cout<<mp[find(i)]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}
E. Alternating String
题目
Sakurako really loves alternating strings. She calls a string $s$ of lowercase Latin letters an alternating string if characters in the even positions are the same, if characters in the odd positions are the same, and the length of the string is even.
For example, the strings ‘abab’ and ‘gg’ are alternating, while the strings ‘aba’ and ‘ggwp’ are not.
As a good friend, you decided to gift such a string, but you couldn’t find one. Luckily, you can perform two types of operations on the string:
- Choose an index $i$ and delete the $i$-th character from the string, which will reduce the length of the string by $1$. This type of operation can be performed no more than $1$ time;
- Choose an index $i$ and replace $s_i$ with any other letter.
Since you are in a hurry, you need to determine the minimum number of operations required to make the string an alternating one.
实现
考虑两种状态,一种n为偶数,一种为奇数,偶数必不进行删除操作,那只需要贪心选最小成本即可,奇数要枚举删除的位置,删完之后的位置奇偶的顺序会发生变化,因此记录一下i号位当前的各字母出现情况,注意区分奇偶序列,从1到n枚举,每次贪心选出最后剩什么字母的成本,取最小即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e5+10;
//const int M=2e5+10;
int dp[N];
int a[N],b[N];
int ch1[N][27];
int ch2[N][27];
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
string s;
cin>>s;
s=' '+s;
map<char,int>mp1;
map<char,int>mp2;
if(n%2==0)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i%2==1) mp1[s[i]]++;
else mp2[s[i]]++;
}
int ans1=0;
int ans2=0;
for(auto it:mp1) ans1=max(ans1,it.second);
for(auto it:mp2) ans2=max(ans2,it.second);
cout<<n-ans1-ans2<<endl;
}
else
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=26;j++)
{
ch1[i][j]=0;
ch2[i][j]=0;
}
if(i%2==1)
{
ch1[i][s[i]-'a']++;
for(int j=0;j<26;j++)
{
ch1[i][j]+=ch1[i-1][j];
ch2[i][j]+=ch2[i-1][j];
}
}
else
{
ch2[i][s[i]-'a']++;
for(int j=0;j<26;j++)
{
ch1[i][j]+=ch1[i-1][j];
ch2[i][j]+=ch2[i-1][j];
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int max1=0;
int max2=0;
for(int j=0;j<26;j++)
{
max1=max(ch2[n][j]-ch2[i][j]+ch1[i-1][j],max1);
max2=max(ch1[n][j]-ch1[i][j]+ch2[i-1][j],max2);
}
ans=max(ans,max1+max2);
}
cout<<n-ans<<endl;
}
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}
F. Sakurako’s Box
题目
Sakurako has a box with $n$ balls. Each ball has it’s value. She wants to bet with her friend that if the friend randomly picks two balls from the box (it could be two distinct balls, but they may have the same value), the product of their values will be the same as the number that Sakurako guessed.
Since Sakurako has a PhD in probability, she knows that the best number to pick is the expected value, but she forgot how to calculate it. Help Sakurako and find the expected value of the product of two elements from the array.
It can be shown that the expected value has the form $\frac{P}{Q}$, where $P$ and $Q$ are non-negative integers, and $Q \ne 0$. Report the value of $P \cdot Q^{-1}(\bmod 10^9+7)$.
实现
我恨取模
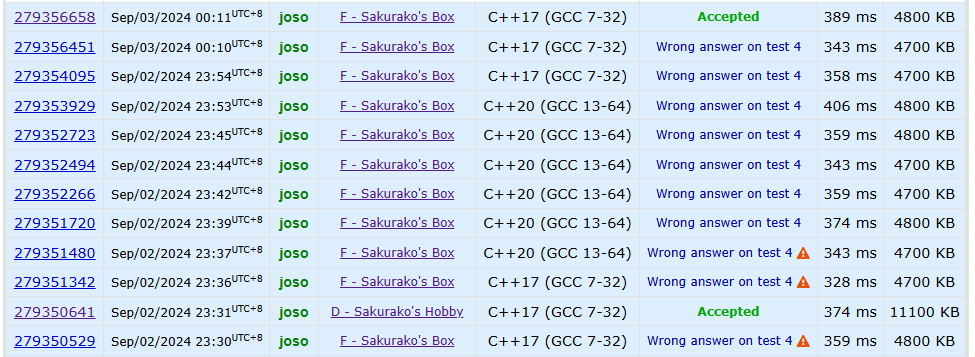
算贡献+组合数+逆元
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e5+10;
int dp[N];
int a[N],b[N];
const int mod=1e9+7;
int quick_pow(int a,int b)
{
int ans=1;
while(b){
if(b&1) ans=(ans*a)%mod;
b>>=1;
a=(a*a)%mod;
}
return ans;
}
int inv(int a,int b)
{
return (a*quick_pow(b,mod-2))%mod;
}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
int sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i],sum+=a[i],sum%=mod;
int num=(n-1)*n/2;
num%=mod;
int d1=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
sum-=a[i];
d1+=(a[i]%mod)*((sum+mod)%mod);
d1%=mod;
}
int ans=inv(d1,num);
cout<<(ans+mod)%mod<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}
G. Sakurako’s Task
题目
Sakurako has prepared a task for you:
She gives you an array of $n$ integers and allows you to choose $i$ and $j$ such that $i \neq j$ and $a_i \ge a_j$, and then assign $a_i = a_i - a_j$ or $a_i = a_i + a_j$. You can perform this operation any number of times for any $i$ and $j$, as long as they satisfy the conditions.
Sakurako asks you what is the maximum possible value of $mex_k$$^{\text{∗}}$ of the array after any number of operations.
$^{\text{∗}}$$mex_k$ is the $k$-th non-negative integer that is absent in the array. For example, $mex_1({1,2,3 })=0$, since $0$ is the first element that is not in the array, and $mex_2({0,2,4 })=3$, since $3$ is the second element that is not in the array.
实现
尽可能让所有的数字变小就是最优解,手动模拟一下会发现最后的数组排列为i*数组最大公因数(0<=i<=n)
将k按顺序插入即是最答案
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N=2e5+10;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int a[N];
int gcd(int a,int b)
{
if(a%b==0) return b;
else return gcd(b,a%b);
}
void solve()
{
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
int num=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!num) num=a[i];
else num=gcd(num,a[i]);
}
if(n == 1)
{
if(k>a[1]) cout<<k<<endl;
else cout<<k-1<<endl;
}
else
{
if(num==1) cout<<n-1+k<<endl;
else
{
int sum=((k+num-2)/(num-1));
sum=min(sum,n);
cout<<k+sum-1<<endl;
}
}
}
signed main()
{
int t=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
}